Understanding Allergies and Intolerances in Infants: A Comprehensive Guide
As parents, ensuring the health and well-being of our infants is of paramount importance. One area that requires careful attention is allergies and intolerances, which can have a significant impact on an infant’s health and development. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the complex world of allergies and intolerances in infants, exploring their causes, symptoms, diagnosis, management, and prevention strategies.
Introduction to Allergies and Intolerances:
Allergies and intolerances are immune system reactions to specific substances that the body perceives as harmful. While allergies involve an immune response to a particular allergen, intolerances occur when the body has difficulty digesting certain foods or components. Both allergies and intolerances can manifest in infants, often presenting unique challenges for parents and caregivers.
Common Allergens and Intolerances:
Some of the most common allergens and intolerances in infants include:
- Food Allergies: Common food allergens in infants include cow’s milk, eggs, peanuts, tree nuts, soy, wheat, fish, and shellfish.
- Food Intolerances: Lactose intolerance, gluten intolerance (celiac disease), and sensitivity to certain food additives are examples of food intolerances that may affect infants.
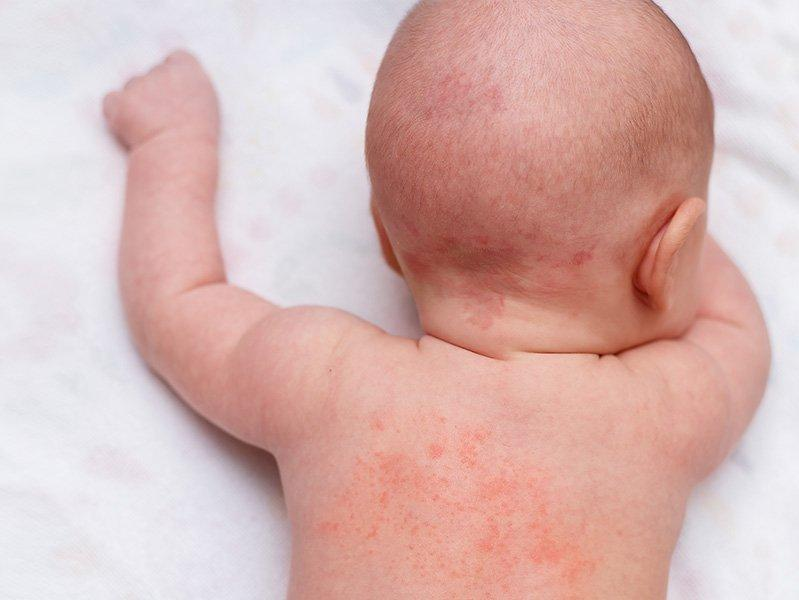
Signs and Symptoms:
Identifying allergies and intolerances in infants can be challenging, as symptoms can vary widely and may overlap with other health issues. Common signs and symptoms of allergies and intolerances in infants include:
- Skin reactions such as hives, eczema, or rash
- Gastrointestinal issues such as vomiting, diarrhea, or constipation
- Respiratory symptoms such as coughing, wheezing, or nasal congestion
- Behavioral changes such as irritability, excessive crying, or sleep disturbances
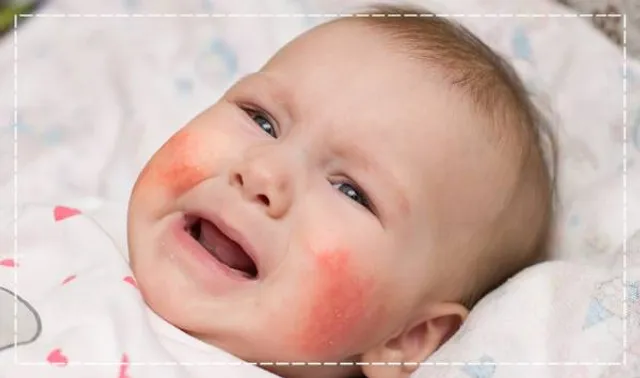
Diagnosis and Evaluation:
Diagnosing allergies and intolerances in infants often requires a comprehensive evaluation, which may include:
- Medical History: A detailed medical history, including family history of allergies or intolerances, can provide valuable insights into potential triggers.
- Physical Examination: A thorough physical examination can help identify any visible signs or symptoms of allergies or intolerances.
- Allergy Testing: Allergy testing, such as skin prick tests or blood tests, may be recommended to identify specific allergens.
- Elimination Diet: In some cases, healthcare providers may recommend an elimination diet to identify potential food triggers by removing certain foods from the infant’s diet and gradually reintroducing them under medical supervision.
Management and Treatment:
The management of allergies and intolerances in infants typically involves:
- Dietary Modifications: For infants with food allergies or intolerances, dietary modifications are often necessary to eliminate triggers from their diet. This may involve avoiding certain foods or using specialized formulas or hypoallergenic products.
- Symptom Management: Depending on the severity of symptoms, healthcare providers may recommend medications such as antihistamines or corticosteroids to alleviate allergic reactions or gastrointestinal symptoms.
- Education and Support: Educating parents and caregivers about allergen avoidance, symptom management, and emergency response procedures is essential for ensuring the safety and well-being of infants with allergies or intolerances.
Prevention Strategies:
While it may not be possible to prevent allergies and intolerances entirely, there are steps that parents can take to reduce the risk:
- Breastfeeding: Exclusive breastfeeding for the first six months of life has been shown to reduce the risk of allergies and intolerances in infants.
- Introduction of Solid Foods: Introducing potential allergenic foods, such as peanuts and eggs, early in infancy (around 6 months of age) may help reduce the risk of developing allergies.
- Avoidance of Tobacco Smoke: Avoiding exposure to tobacco smoke during pregnancy and after birth can help reduce the risk of respiratory allergies in infants.
Conclusion:
Allergies and intolerances can pose significant challenges for infants and their families, impacting their health, quality of life, and overall well-being. By understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, management, and prevention strategies related to allergies and intolerances in infants, parents and caregivers can take proactive steps to support their child’s health and development. Working closely with healthcare providers, educating themselves about allergen avoidance and management strategies, and seeking support from peers and support groups can help navigate the complexities of allergies and intolerances in infants and provide the best possible care for their little ones.

